
Thesis Report on Radionuclide Distribution & Health Risk in Dharla River Sediment of Bangladesh.
With the course of time the structure of the earth was modified through various geological and atmospheric incidents and changes. The Earth formed from a mixture of dust and gas encircling the early sun more than 4.6 billion years ago. It grew as a result of several collisions between dust grains, asteroids, and newly formed planets. In these terms, the various geological incidents like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions have been the reasons behind the present geological condition of the earth and also various natural radio activities in the soil of different places.
| Report Title : | Radionuclide Distribution & Health Risk in Dharla River Sediment, Bangladesh. |
| University Name : | Bangladesh University of Professionals (BUP) |
| Submitted To : | Dr. Md. Mostafizur Rahman |
| Submitted By : | Mithila Farzana |
| Total Page : | 94 |
The internal structures of unbalanced or radioactive isotopes are the source of ionizing radiation. The surplus internal energy in these atoms’ nuclei causes spontaneous moderations that release more energy in the form of beta, gamma, or alpha particles a condition known as radioactivity. Globally, there are variance in the amounts of natural ambient radioactivity and exogenous exposure to gamma radiation due to regional geological and geographical factors.
Problem Statement
The ecosystem contains naturally occurring radioactivity from NORMs in a variety of geological evaluation including soils, minerals, water, sediments, air, and building materials. Among other things nuclear weapon testing circumstance involving nuclear weapons and industrial and medical uses are the sources of artificial radionuclides. According to El Samad et al artificial radionuclides created by human activity and naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORMs) expose living things to a wide range of ionizing radiations on a regular basis.
Outline of the Study
Introduction Part
Background of the study, Problem statement, Rationale of the study, Research Questions, Research Hypothesis, Objectives of the study, Limitations of the Study, Explanation of Important Terms Used, Outline of the thesis.
Literature review Part
Review of existing literature, Research Gap Analysis.
Methods and Methodology Part
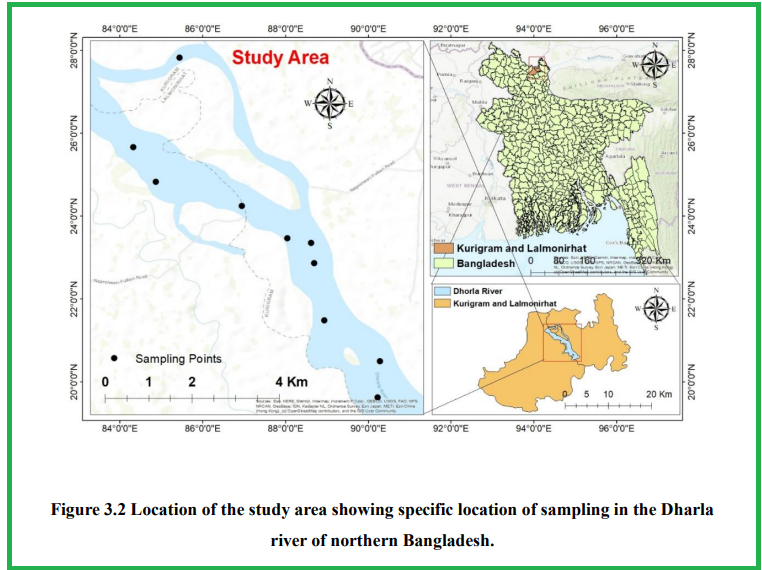
Research Design, Study Area Location, Sample Collection Procedures, Steps of Sample Preparation, Drying, Sieving, 3.4.3 Grinding, Weighing, Preparation of Sample for HPGe Detector, Setup of the experiment, High Purity Germanium detector (HPGe), Standard Gamma Ray sources, Detector Parameters Calibration, HPGe Detector Efficiency Calibration, Lower Limit of Detection (LLD) of Radionuclides, Gamma Ray Detection, Preparation of sample for INAA, Experimental setup for INAA, Application of INAA, Irradiation, Counting, Concentration Calculation, Accuracy and Precisions, Secondary data sources.
Analysis Part
Various Radiological and Environmental Indicators, Raeq or Radium equivalent activity, External hazard index (Hex) and Internal hazard index (Hin), Absorbed dose rate (D), Eaed or Annual effective dose rate, Gamma representative level index (Iγ), Activity utilization index (AUI), Excess lifetime cancer risk (ELCR), Statistical analysis.
Result and Discussion Part
Statistical analysis result of occurrence and NORMs distribution, Radiological Risk , Policy Implications
Conclusion & References Part
Research Questions
- Taking into account the research challenges and important gaps in previous studies, the following primary research questions are expressed.
- What are the natural radionuclide attentiveness in the Dharla River sediment?
- What is the concentration of elements in the Dharla River basin?
- How are the natural radioactivity levels and study metal distributions distributed geographically in the Dharla River sediments described?
- Based on radiation health hazard indices (ELCR), what health hazards do locals and tourists have from naturally occurring radionuclides (such as 40K, 232Th, and 226Ra)?
- What may be deduced about the degree of contamination and pollution in the Dharla River from an evaluation of elemental abundances?
Objectives of the study
- In order to determine the Tran’s boundary river Dharla’s inclination or declination with respect to other rivers, the main goal of this study is to influence the concentration of naturally occurring radioactive materials, such as 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K. The objectives of the study are as follows.
- To observe baseline data on radionuclides found in the Dharla River naturally.
- To determine the chemical composition of the Dharla riverbed sediment samples that are collected by INAA.
- To investigate the distribution of naturally occurring radioactivity in the sediments of the Dharla River.
- To evaluate the radiation health hazard status and the degree of contamination and assess the health risks posed by naturally occurring radiation.
- To assess the excess lifetime cancer risk (ELCR) and the radiation-related health hazards indexes in the assigned study region and understand their reaction on human health.
Conclusion
Generally the results point to a complex interaction between human and natural variables influence the distribution of radionuclides in the dregs of the Dharla River. The instructions provided here is extraordinarily helpful in managing and monitoring the environment, as it helps to define the possible concerns related to radioactivity in this aquatic ecosystem. Still more investigation and monitoring are needed to provide a more thorough evaluation of the future implications of human activity on the radiological profile of the river.







